What is an anal fissure?
An anal fissure is a “cut” or “tear” at the anus or inside the anal canal. It is a very common proctological problem.
The condition is sometimes misdiagnosed as hemorrhoids as they share several symptoms, especially when a “skin tag” is present.
Sometimes, physical examination is not enough to get an accurate diagnosis, and your doctor may need to visualize the lesion with anoscopy.
Acute Fissures may develop into chronic fissures. Over 90% of acute fissures last for a short duration and heal spontaneously or with simple self-care measures.
However, if you leave anal fissures untreated, they can become chronic and cause a myriad of problems.




Chronic fissure symptomatic
circulation

Chronic fissure pathological slow healing circulation

What are the symptoms of anal fissure?
During your initial assessment, the doctor at our clinic will investigate the possible cause of the fissure and determine its exact location. Based on a variety of factors, your doctor will determine the best course of action in the treatment of your anal fissure.
The most common symptoms of anal fissures include Pain, Bleeding, Itching, and constipation.
You can self-assess how serious your anal fissure is based on your symptoms. It is essential to treat it early instead since a slow-healing anal fissure could reduce the chances of successful non-invasive procedures.
- Pain: Pain is extremely severe after the bowel movement. is typical.You will experience pain at the beginning of pushing out the stool and while passing the stool. After a few minutes, it becomes more excruciating than ever and persists for a few hours. Sometimes, the pain radiates to the pelvic floor and causes difficulty urinating. The pain can be burning, stabbing, piercing, or dull. It can also develop when walking, sitting, coughing, or passing gas.
- Anal Bleeding: Consists of a streak of bright red blood on toilet paper or the stool.
- Anal Itching/Pruritus ani: anal itching in the perianal region is caused by the irritation of the anal mucosa. The anal region will feel unclean and always wet. In addition, the secondary changes from the chronic fissure (e.g., enlarged anal papillae, fistula) cause stool soiling.
- Constipation: This is mediated by a fear of having a bowel movement due to the severe pain.
- Purulent discharge: If an anal abscess or anal fistula is associated with your anal fissure, you will experience severe pain, fever, swelling, and discharge of pus mixed with blood.
- Overall emotional symptom: The pain affects the patient during rest, and some patients are afraid of eating and losing weight due to fear of defecation.
What are the types of anal fissures?
Defined by time: Acute and Chronic
Acute Fissure – occurs with a sudden onset and healing within 2-6 weeks.
Chronic Fissure – Generally fails to heal within 8 weeks. Chronic anal fissure is inconsistent in its symptoms.
Defined by location
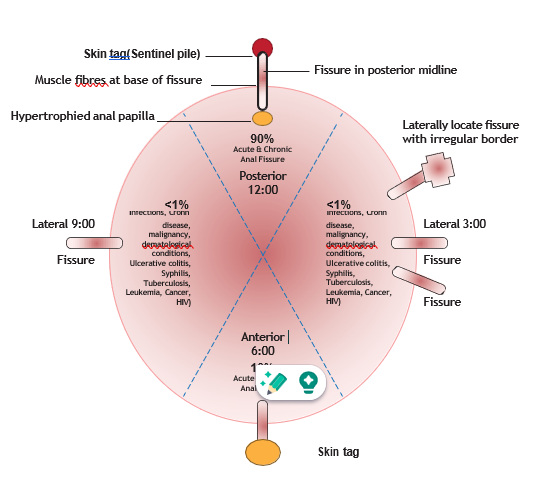
Most fissures are located at the back (i.e., posterior fissures), although they can also be located at the front (i.e., anterior fissures) or at the sides. Anal fissures can also be in more than one location. The location may give us a clue to the cause of the anal fissure. For example, a fissure located at the sides may be more likely due to Crohn’s disease.
Defined by number:
Singular anal fissure.
Multiple anal fissures.
Defined by disease-caused anal fissure:
Simple anal fissure.
Complicated anal fissures (e.g., anal fissures due to viral infections).
Defined by recognition:
Visible anal fissure.
Invisible anal fissure..
Who is more prone to have fissures?
What are the causes of anal fissures?
Primary Causes:
- Constipation
- Chronic Diarrhea
- Anal itchiness/Anal eczema
- Childbirth
- Anal trauma
- Penetration
- Hemorrhoids
- Anal skin tag
- Anatomic anal setonese
** In addition to the factors listed, primary fissures may also have no clear underlying cause.
Secondary Causes:
- Irritable Bowel Disease (IBD)-more common in Crohn’s Disease
- Granulomatous Diseases-Such as extrapulmonary tuberculosis, sarcoidosis
- Granulomatous Diseases-Such as extrapulmonary tuberculosis, sarcoidosis
- Communicable diseases—Such as HIV infection, syphilis, chlamydia
- Sexually transmitted diseases (STIs)
- Drug-Induced: Ergotamine, Nicorandil, Isotretinoin, Chemotherapeutics
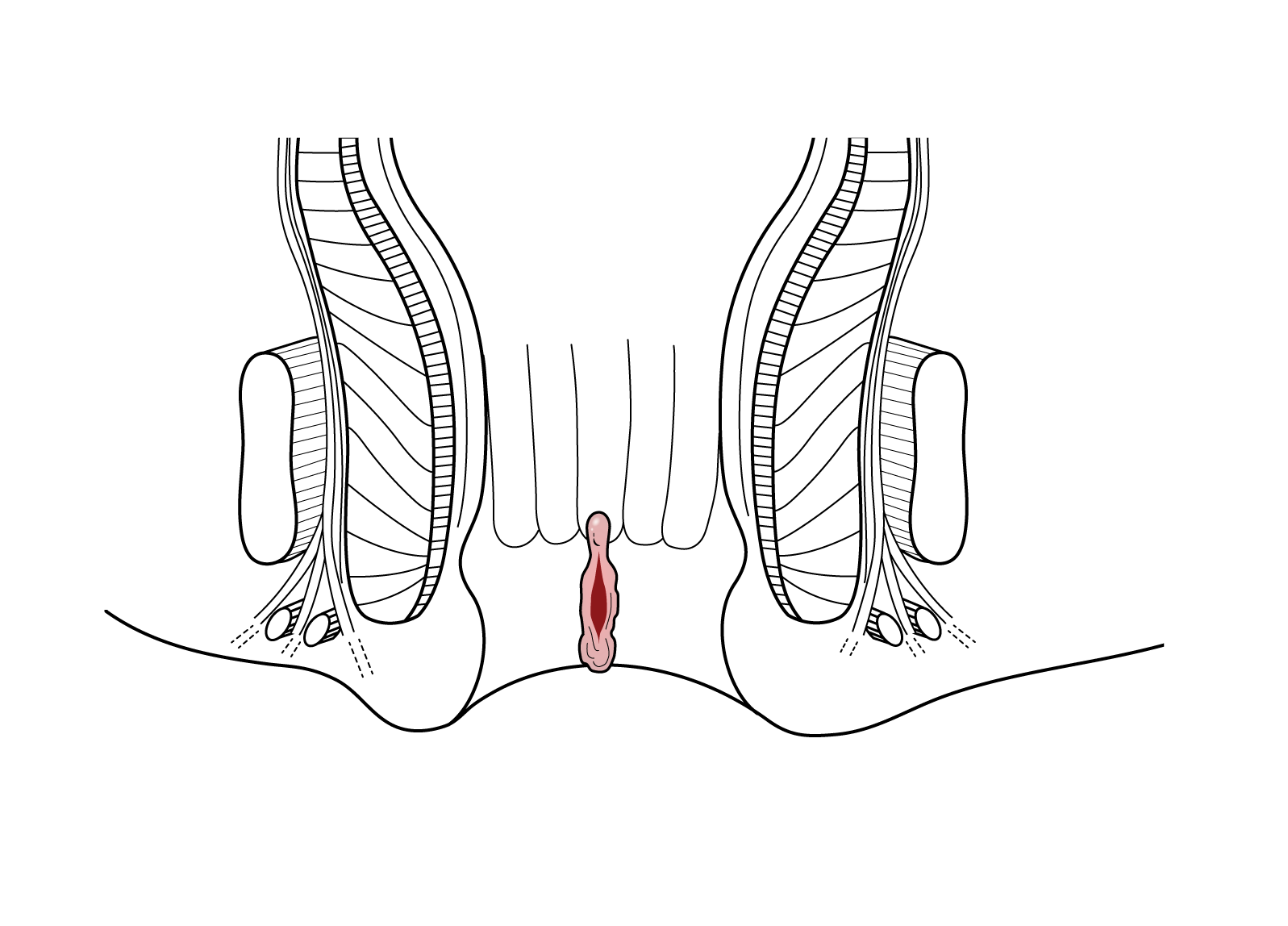
Chronic Anal fissure secondary changes
Some facts about anal fissures
- Sentinel Pile/hemorrhoid/tag
- Anal Cryptitis
- Hypertrophied Anal Papilla/Anal Papillitis
- Anal abscess
- Anal Fistula
- Chronic fissures are wider and deeper than acute fissures and have raised edges that may be swollen. Sphincter muscle fibers may be visible at the base of a chronic fissure. The proximal end of a chronic anal fissure may be hypertrophied anal papillae, while a skin tag (sentinel pile) may be at the distal end.
- Typical fissures are usually singular. They generally occur in the posterior midline and less commonly in the anterior midline. They are also more common in women.
- Atypical fissures (multiple, laterally located. or with irregular borders) may indicate a secondary cause.
- A fissure isn’t always visible and does not need to be seen for a diagnosis to be made. For instance, anal spasms and/or pain may make it difficult to visualize the fissure. The patient’s straining can sometimes reveal the fissure. Additionally, gentle pressure on the anal margin may produce pain.
- For patients with chronic anal fissures who are unlikely to have a secondary cause, the vicious cycle of pain and spasm prevents healing. Therefore, the goals of treatment are to relieve spasms and improve blood supply to the fissure.
- A change in lifestyle and toilet habits should be associated with serious treatment – Treating any underlying cause, such as constipation, is indispensable.
- Most “typical” anal fissures occur in the anterior or posterior midline. Lateral fissures indicate a less common etiology (e.g., IBS, STIs, malignancy).
Our Anal Fissure Treatment- Guoyi Proctology Therapy
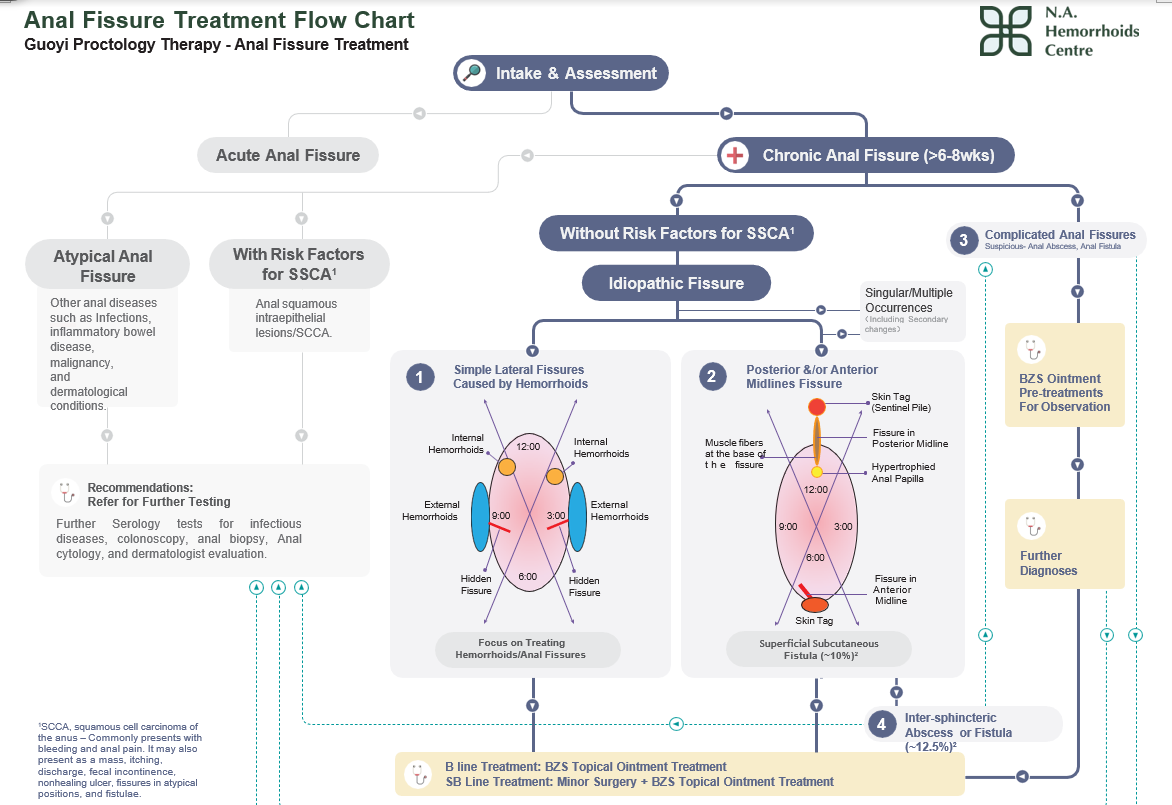
Guoyi Proctology Grading System for Anal Fissure
Grade 1: Acute fissure- Fresh cut
Within 6-8 weeks, the tear is fresh and simple, whereas elasticity is poor, so no chronic ulcer is formed. The fibers of the longitudinal muscle are exposed on the wound surface.
Grade 2: Ulcer forming stage
The wound edge is raised with induration. Wound granulation tissue is not fresh and there are apparent ulcers.
Grade 3: Ulcer formed stage
In old chronic anal fissures with a history of recurrence, the base of the fissure is deep and the wound’s margin is irregular, hard, and stiff. Complications may arise due to the inflammation. Examples include sentinel Pile, hemorrhoids, hypertrophied papillae, anal cryptitis, and subcutaneous fistula.
Grade 4: Ulcer with multiple complexities
Aside from the symptoms of grade 3 anal fissures, the fissures will cause complications, which present with superficial subcutaneous fistula and true fistula.
- Superficial subcutaneous fistula
- Sentinel Pile/hemorrhoid/tag
- Anal abscess and Anal Fistula
Examination Position

Knee-chest

Standing

Side-lying

Knee-chest, Side-lying
The features of Guoyi Proctology Therapy
The benefits of our anal fissure treatment
We Focus on the full solution and cure of prolonged fissures; we also assist you in determining the source or receiving additional medical care attention.
- Instant benefit: Relief from pain, bleeding
- Mid-term benefit: Lower the risk of chronic anal fissures.
- Long-term benefit: Focus on complete resolution and prevention of reoccurrence.
- Discovery of hidden anal abscess or anal fistula and present treatable options
- Clear “exit” solution
- Together treating the associated issue, such as internal and external hemorrhoids, anal abscess etc.
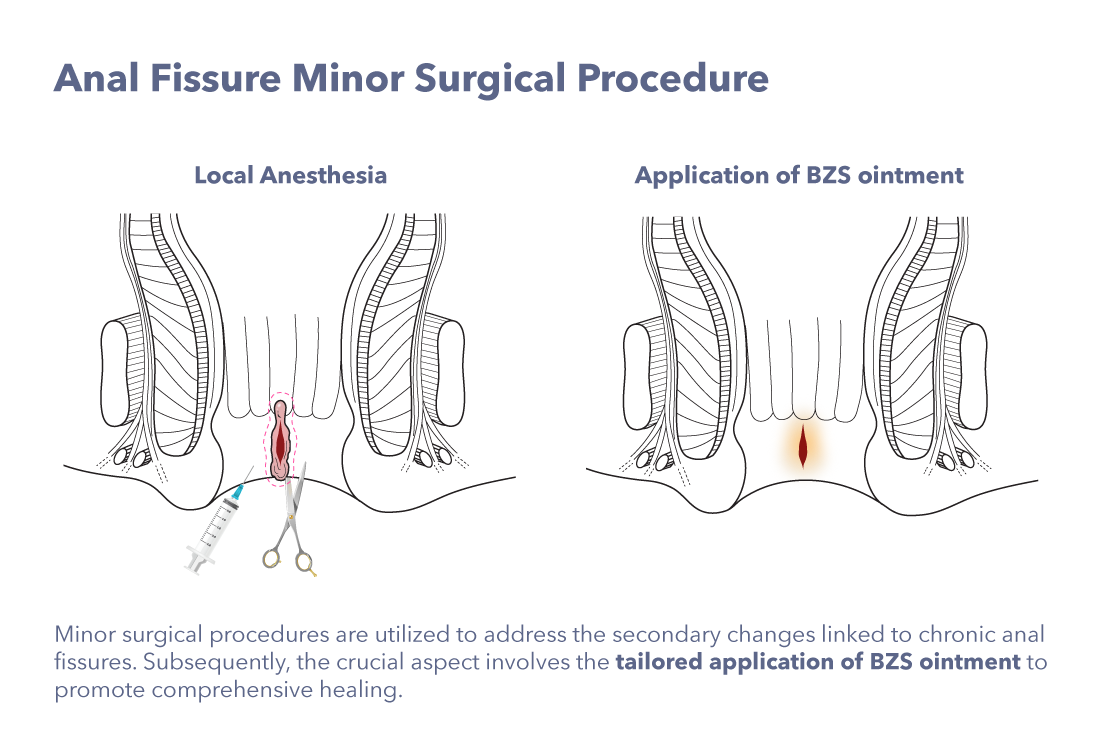
We operate minor Surgical Procedure if needed:
- Remove the physical cause of the anal fissure.
- Dissolve chronic hard tissue with minor surgery and botanical herbal ointment.
- Ease the spasm without damaging the internal sphincter.
- Treat inflamed tissue, such as hypertrophied anal papilla, anal cryptitis, and sentinel skin tag
- Minimize the discomfort and complications.
The treatment will be “specialized Ba Zhi San ointment” centered.
- Individualized Ba Zhi San ointments application plan
- Increase the local blood flow within the anus.
- Allow the ulcer to heal.
- Speed up the healing course.
- Release the pressure from the sphincter muscle.
Anal fissure prevention
- Do your best to prevent constipation or diarrhea. Get treatment for chronic constipation or ongoing diarrhea.
- Stay hydrated. Too much alcohol and caffeine can lead to dehydration.
- Don’t ignore your urge to go.
- Don’t strain or sit on the toilet for too long.
- Gently clean and dry the anal region after each bowel movement.
- Avoid irritants to the skin, such as scented soaps or bubble baths.
- Use our clinical 20ml Enema when you feel you have to push very hard.
- Immediate self-care when acute fissure happens.
- Do the Sitz baths for 5 minutes after the Bowel Movement.
- Apply MaYinLong Cream on the visible tear.
- Registered patients can call N.A. Hemorrhoid Clinic Service Line for personalized management.
We can help with your hemorrhoids
We specialize in anorectal diseases and offer therapies for the treatment and prevention of hemorrhoids, anal fistulas, anal fissures, anal abscesses and anal itching caused by anal eczemas.
Fill up the form below and our friendly staff members will get back you you shortly to arrange an appointment that works best for you.


